BLOG

The alarming surge of Phishing and how to protect your business
The threat of phishing is escalating. Statista reported that there were over 1.62 million unique phishing sites globally in Q1 2023, over 50% higher than the same period in 2022. On top of that, a 2024 survey involving 500 cybersecurity experts indicates a staggering 94% of organizations have faced phishing attacks.
Almost 80% of organizations faced financial implications due to phishing, with 64% experiencing direct monetary loss. Of these incidents, 74% led to disciplinary actions against employees.
Businesses typically spend about 11 months recovering from a phishing attack. With such implications, phishing has now become the primary method for initiating breaches (16%), surpassing stolen credentials (15%), according to data retrieved by IBM. The 2023 data also revealed that data breaches cost an average of over $4.5 million.
Types of phishing attacks
Phishing attacks come in various forms. Each of these has its own distinct characteristics. Here are some common types:
- Email Phishing: The most common type, where attackers send fraudulent emails resembling those from reputable sources. These emails aim to trick recipients into revealing sensitive information, such as passwords or credit card numbers.

- Spear-Phishing: A targeted form of phishing. Attackers personalize emails to specific individuals, often using personal information for authenticity. The goal is to steal data or install malware on the target’s device.
- Whaling: A specialized spear-phishing attack targeting high-profile individuals like executives. Whaling attacks often involve crafting highly sophisticated emails that address specific business concerns or personal interests of the target.
- Smishing (SMS Phishing): This type of phishing attack uses text messages instead of emails. Smishing messages often create a sense of urgency, prompting recipients to disclose personal information or click on a malicious link.
- Vishing (Voice Phishing): Conducted via phone calls. Attackers pretend to be from legitimate organizations, seeking personal or financial information. They often use fear tactics, like threatening legal action.
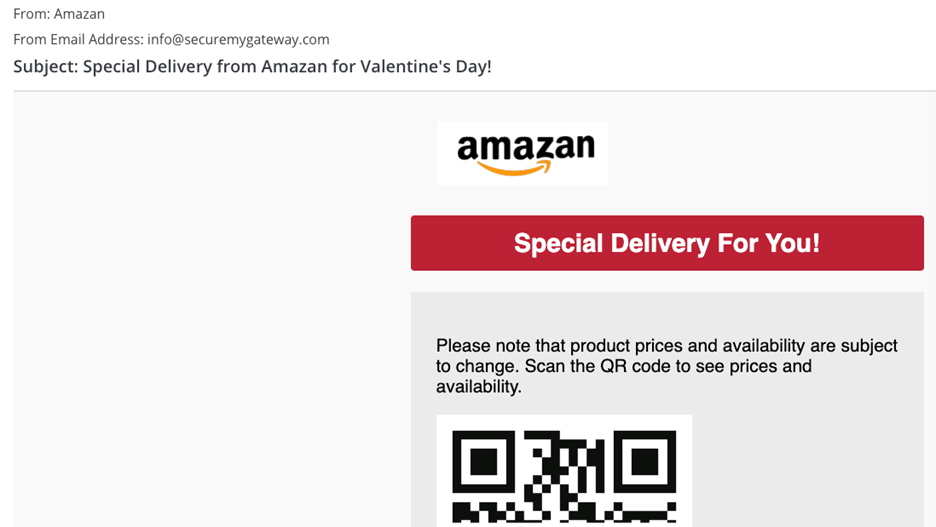
- Quishing: This involves the use of fake or manipulated QR codes whereby hackers carry out fraudulent activities, such as malware spreading or taking personal information.
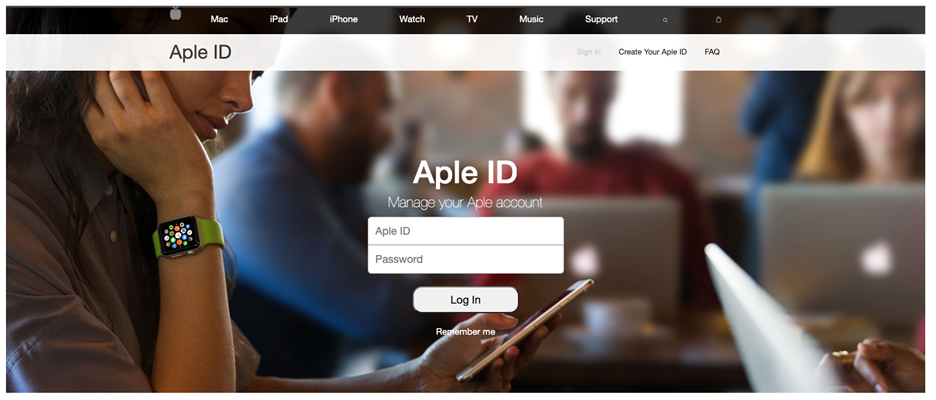
- Pharming: Here, attackers redirect users from legitimate websites to fraudulent ones. This is typically achieved by exploiting vulnerabilities in DNS servers.
- Clone Phishing: Involves creating a nearly identical replica of a legitimate email with a safe attachment or link replaced by a malicious one. It often claims to be a resend or updated version of the original.
- Angler Phishing: Uses social media platforms for attacks. Fraudulent social media posts or messages, often pretending to be customer service accounts, aim to extract personal information from victims.
Well-known cases of phishing
Deepfake video attack
A multinational company recently lost $26 million after a Deepfake fooled employees, fabricating representation of the CFO and others. The scammers convinced the victim to make a total of 15 transfers to five different Hong Kong bank accounts, according to reports. The company attacked has not been identified.
Colonial Pipeline attack
In May 2021, the Colonial Pipeline ransomware attack starkly demonstrated the real-world impact of cyber attacks. The attack disrupted fuel supply across the East Coast of the United States. The breach, which likely began with a phishing email, compromised the company’s business network and billing system. Despite Colonial Pipeline paying about $4.4 million for a decryption key, the ripple effects were far-reaching.
The shutdown, lasting a week, halted the delivery of around 20 billion gallons of oil valued at about $3.66 billion. This incident spiked petrol prices and left over 10,000 petrol stations without fuel even after operations resumed. CEO Joseph Blount, in an interview with The Wall Street Journal, acknowledged the wider economic toll and defended his controversial decision to pay the ransom. This attack ranks as one of the most financially devastating phishing incidents ever.
NotPetya Malware attack
June 2017 saw the onset of NotPetya, a catastrophic cyber attack that rapidly spread across more than 60 countries. Originating as a supply chain attack through Ukrainian accounting software, NotPetya targeted Windows-based systems, encrypting hard drives and demanding ransoms. Unlike typical ransomware, NotPetya, likely a state-sponsored Russian wiper malware, rendered data irretrievable. This caused unprecedented damages exceeding $10 billion. Major companies like Maersk, Merck and FedEx suffered immense losses.
Sony Pictures attack
In November 2014, Sony Pictures fell victim to the ‘Guardians of Peace’ hacking group. The attackers gained access through phishing emails, eventually leaking 100 terabytes of sensitive data. The emails, disguised as communications from Apple, deceived top executives into providing their credentials on a fake website. This breach not only exposed employee and film information but also included a demand to withdraw “The Interview” under threats of violence. The total damages to Sony Pictures from this cyberattack were estimated to exceed $100 million.
Facebook and Google scam
Evaldas Rimasauskas, a Lithuanian man, orchestrated a cunning business email compromise (BEC) scam against Facebook and Google, defrauding them of over $100 million. Between 2013 and 2015, Rimasauskas and his associates created convincing forged email accounts. They pretended to be Quanta Computer, a real vendor for both tech giants. Through elaborately crafted phishing emails containing bogus invoices and contracts, they deceitfully billed millions of dollars. The scam resulted in these companies transferring the funds to Rimasauskas’ sham company accounts spread across multiple countries.
FACC business email compromise attack
In 2016, FACC, an Austrian aerospace manufacturer, was hit by a severe BEC attack. Impersonating the CEO, attackers convinced an employee to transfer roughly $50 million for a fake acquisition project. While $10 million was salvaged at the last minute, the company still suffered significant financial damage and the CEO was subsequently dismissed.
Tips to combat phishing
Phishing poses a significant threat to businesses of all sizes. However, companies can effectively combat this pervasive cyber threat through a blend of technological solutions, employee education and vigilant practices. Here’s what businesses can do to combat phishing:
- Recognize phishing scams: Stay informed about new phishing techniques and their common features. Regular updates and training can help you identify these threats early.
- Provide security awareness training: Technical defenses alone can’t stop phishing. Educate employees about phishing dangers and teach them to report suspicious activities. Regular simulated phishing exercises can test and enhance your team’s readiness.
- Strong passwords and Two-Factor Authentication: Encourage unique, complex passwords for each account and discourage password sharing. Implement two-factor authentication for an added security layer.
- Heed update alerts: Don’t ignore software update notifications. These updates often contain vital security patches protecting against the latest cyber threats.
- Be careful with emails and links: Avoid emails and links from unknown sources. Verify links by hovering over them and avoid clicking unless sure of their safety.
- Avoid unsecured websites: Don’t share sensitive information on websites without HTTPS encryption or a visible security certificate. There is a closed padlock icon on the URL bar when the website has HTTPS certification.
- Ignore pop-ups: Pop-ups can be phishing attempts. Use ad-blockers to prevent them and avoid clicking on any that slip through.
- Regularly change passwords: Regularly updating your passwords can prevent ongoing unauthorized access, especially if your accounts have been compromised without your knowledge.
- Deploy Anti-Phishing tools: Use anti-phishing technologies to block fraudulent sites and emails. Combine desktop and network firewalls for comprehensive protection from external threats.
SafeBait: How C8 Secure can help
Partnering with C8 Secure can significantly enhance your company’s defense against phishing attacks. Our SafeBait service offers a comprehensive, managed solution that focuses on both technological and human elements. Our key features include:
- Simulation: Customized simulations help combat various social engineering threats. Our Phishing Simulator offers AI-driven scenarios in over 160 languages. We also have an Email Threat Simulator that strengthens email gateways against cyber attacks.
- Awareness training: Focusing on the human element, C8 Secure’s training includes MFA, Smishing, Vishing and Quishing Simulators. These simulate real-life scenarios and enhance staff’s ability to identify and respond to threats. On top of that, a Security Awareness Training Platform with interactive modules fosters a security-conscious culture.
- Threat sharing: C8 Secure’s Threat Sharing Platform allows for a collaborative defense ecosystem, where clients exchange threat intelligence. This unique approach allows our ecosystem to improve its collective security measures.
Choose C8 Secure’s SafeBait for advanced, all-around defense against phishing. Our simulations, awareness training and threat-sharing platform build a secure, informed company environment. Get in touch today info@c8secure.com.
RECENT POSTS
A year in review: Cybersecurity trends and challenges in 2023
The year 2023 marked a significant evolution in the cybersecurity landscape as it adapted to an array of emerging digital threats.
DOWNLOAD BROCHURE
For more information, please download our solutions brochure










